Solid lubricants mainly refer to solid substances that can provide lubrication under high temperatures or extreme environments. They generally have higher melting points, thermal and chemical stability. Solid lubricants mainly include the following categories:
Metal powder lubricants: such as lead powder, tin powder, lead-tin alloy, etc., which serve as lubricating phases in mechanical alloys to reduce friction between metals.
Inorganic lubricants: such as graphite, molybdenum disulfide, talc, mica, asbestos, etc. These substances can still maintain lubricating properties in high temperature environments.
Organic polymer lubricants: such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, have excellent chemical stability and low friction coefficient.
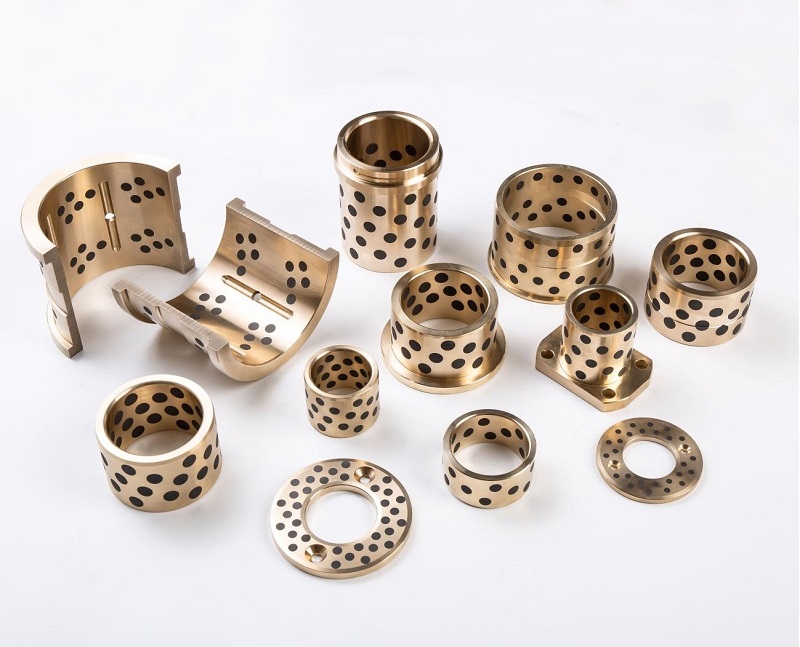
Composite solid lubricant: This type of lubricant usually combines metal powder, inorganic lubricant and organic polymer to obtain better lubrication performance.
Solid lubricants are widely used in aerospace, automobiles, machinery manufacturing and other fields, and can be used to make
solid lubricated bearings and other products. When selecting and using solid lubricants, the most appropriate type should be determined based on the specific application environment and performance requirements.
The future development trends of solid lubricants may include the following aspects:
High performance: With the advancement of science and technology and the continuous complexity of industrial applications, the performance requirements for solid lubricants are also constantly increasing. Future solid lubricants will need to have higher melting points, better chemical stability and lower friction coefficients.
Composite: By combining different types of solid lubricants, you can give full play to their respective advantages, improve lubrication performance, and solve the problems that may exist with a single lubricant.
Environmentally friendly: With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, the development of solid lubricants will pay more attention to environmental protection performance and reduce the impact on the environment, such as reducing the release of harmful substances.
Intelligence: With the development of intelligent manufacturing technology, solid lubricants may be combined with intelligent components such as sensors and controllers to achieve real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment of lubrication status.
Long life: Under extreme conditions such as high temperature, high pressure, and high speed, solid lubricants need to have a longer service life, reduce replacement frequency, and reduce maintenance costs.
Application of nanotechnology: The application of nanotechnology can make the microstructure of solid lubricants more uniform and improve its lubrication performance and wear resistance.
New material development: With the continuous development of new material technology, new solid lubricant materials may appear, which will have unprecedented performance and bring new breakthroughs in lubrication technology.
Green manufacturing and recycling: The manufacturing and recycling process of solid lubricants will pay more attention to green environmental protection and reduce energy consumption and waste emissions.

The future development of solid lubricants will be closely integrated with high technology to meet the needs of various industries for high-performance, environmentally friendly, and intelligent lubrication solutions. At the same time, it will also strengthen cross-integration with material science, nanotechnology, environmental science and other related fields to promote the continuous development of lubrication technology.




 English
English Español
Español


















Contact Us